USB is “Universal Serial Bus”, The Chinese name is called Universal Serial Bus. This is a new interface technology widely used in PC field in recent years. USB port has the characteristics of faster transmission speed, support hot swap and connect multiple devices. It has been widely used in all kinds of external devices. There are three types of USB ports: USB1.1, USB2.0, and more recently USB 3.0. Theoretically, USB1.1 can deliver speeds of up to 12Mbps/ SEC, while USB2.0 can deliver speeds of up to 480Mbps/ SEC, and is backward compatible with USB1.1.
As computer hardware develops at full speed, peripheral equipment increases day by day, keyboard, mouse, modem, printer, scanner is already known to all, digital camera, MP3 walkman comes one after another, so many equipment, how to access personal computer? USB was created for this purpose.
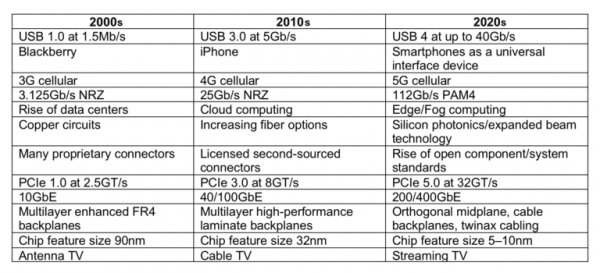
USB connector development and evolution in the last 20 years
Any computing device can be severely slowed down by its limited ability to receive and transmit data to the outside world. Data bottlenecks on input/output (I/O) panels limit information transfer and make devices less efficient. Over the years, the 15 – and 25-pin D-Sub connectors have changed in their ability to provide peripherals with adequate I/O transmission data rates. Originating in military applications, these Mil-Spec connectors feature reliable pin and socket connections, as well as rugged housing. Modifying these Mil-Spec connectors to commercial versions and pricing them to the consumer level makes them the de facto consumer product standard, which is now widely used in video, computer accessories and more. As the demand for data rates increases from kilobytes to megabytes, less space is available for external interconnections, requiring new connector interfaces. In 1996, usB-IF, a consortium of electronics industry leaders, was born and released the first generation OF USB ports. The first release was an improved USB1.1 specification intended to replace the array interface, which adversely affected compatibility between extended peripherals, including flash and external hard drives, scanners and printers. The connection is made through a relatively small rectangular connector with an initial transfer rate of 1.5Mb/s, using a low insertion force connection with a lifetime of about thousands of times, but only in one direction.
A major advantage of the USB standard is the ability to transmit power and signals simultaneously, enabling remote devices to operate without external power. The “hot plug” capability is another key feature of USB ports.
Not content with existing standards, USB-IF released the USB 4 specification in September 2019. The connector will maintain the Type-C interface, but will integrate Intel Thunder 3 with 40GB/s transfer rate technology. USB 4 is backward compatible with THE USB Type-C protocol, including USB 3.2, DisplayPort, and Thunder 3, simplifying connectivity for a whole new generation of devices. Devices with this new interface are expected by 2021.
Usb-if demonstrates its commitment to continuous upgrades, enabling USB to continue to play a key role in the design of the next generation of devices.
That’s the 20-year history of USB connectors. With the continuous development of global technology, the replacement of electronic products. Future USB connectors will also be updated to meet higher requirements.
Post time: Jan-04-2022